Nanjing Massacre
| Nanjing Massacre Rape of Nanjing | |
|---|---|
| Part of the Second Sino-Japanese War | |
 A Japanese soldier pictured with the corpses of Chinese civilians by Qinhuai River | |
| Location | Nanking, China |
| Date | From December 13, 1937, for six weeks [note 1] |
Attack type | Mass murder, wartime rape, looting, and arson |
| Deaths | 200,000 (consensus), estimates range from 40,000 to over 300,000. |
| Perpetrators |
|
| This article is part of the series on |
| Nanjing Massacre |
|---|
| Japanese war crimes |
| Historiography of the Nanjing Massacre |
| Films |
| Books |
The Nanking Massacre or the Rape of Nanking[2] was the mass murder of Chinese civilians in Nanking, the capital of the Republic of China, immediately after the Battle of Nanking in the Second Sino-Japanese War, by the Imperial Japanese Army.[3][4][5][6] Beginning on December 13, 1937, the massacre lasted six weeks. The perpetrators also committed other war crimes such as mass rape, looting, and arson.[note 1] The massacre was one of the worst atrocities committed during World War II.[7]
Due to a myriad of factors, death toll estimates vary from 40,000 to over 300,000, with rape cases ranging from 20,000 to over 80,000 cases. However, most credible scholars in Japan, which include a large number of authoritative academics, support the validity of the International Military Tribunal for the Far East and its findings, which estimate at least 200,000 murders and at least 20,000 cases of rape.[3][8][9]
Military situation
In August 1937, the Japanese army invaded Shanghai, where they met strong resistance and suffered heavy casualties. The battle was bloody as both sides faced attrition in urban hand-to-hand combat.[10] By mid-November, the Japanese had captured Shanghai with the help of naval and aerial bombardment. The General Staff Headquarters in Tokyo initially decided not to expand the war due to the high casualties incurred and the low morale of the troops.[11] Nevertheless, on December 1, headquarters ordered the Central China Area Army and the 10th Army to capture Nanking, then-capital of the Republic of China.
Relocation of the capital
After losing the Battle of Shanghai, Chiang Kai-shek knew that the fall of Nanking was a matter of time. He and his staff realized that they could not risk the annihilation of their elite troops in a symbolic but hopeless defense of the capital. To preserve the army for future battles, most of it was withdrawn. Chiang's strategy was to follow the suggestion of his German advisers to draw the Japanese army deep into China and use China's vast territory as a defensive strength. Chiang planned to fight a protracted war of attrition to wear down the Japanese in the hinterland of China.[12]
Strategy for the defense of Nanking
In a press release to foreign reporters, Tang Shengzhi announced the city would not surrender and would fight to the death. Tang gathered about 100,000 soldiers, largely untrained, including Chinese troops who had participated in the Battle of Shanghai. The Chinese government left for relocation on December 1, and the president left on December 7, leaving the fate of Nanking to an International Committee led by John Rabe, a German national.
In an attempt to secure permission for this cease-fire from Generalissimo Chiang Kai-shek, Rabe, who was living in Nanking and had been acting as the Chairman of the Nanking International Safety Zone Committee, boarded the USS Panay (PR-5) on December 9. From this gunboat, Rabe sent two telegrams. The first was to Chiang through an American ambassador in Hankow, asking that Chinese forces "undertake no military operations" within Nanking. The second telegram was sent through Shanghai to Japanese military leaders, advocating for a three-day ceasefire so that the Chinese could withdraw from the city.
The following day, on December 10, Rabe got his answer from the Generalissimo. The American ambassador in Hankow replied that although he supported Rabe's proposal for a ceasefire, Chiang did not. Rabe says that the ambassador also "sent us a separate confidential telegram telling us that he has been officially informed by the Foreign Ministry in Hankow that our understanding that General Tang agreed to a three-day armistice and the withdrawal of his troops from Nanking is mistaken, and moreover that Chiang Kai-shek has announced that he is not in a position to accept such an offer." This rejection of the committee's ceasefire plan, in Rabe's mind, sealed the fate of the city. Nanking had been constantly bombed for days and the Chinese troops that remained there were disheartened and had taken to drinking before the city's inevitable fall.
On December 11, Rabe found that Chinese soldiers were still residing in areas of the Safety Zone, meaning that it became an intended target for Japanese attacks despite the majority being innocent civilians. Rabe commented on how efforts to remove these Chinese troops failed and Japanese soldiers began to lob grenades into the refugee zone.[13]
Approach of the Imperial Japanese Army
Japanese war crimes on the march to Nanking


Although the massacre is generally described as having occurred over a six-week period after the fall of Nanking, the crimes committed by the Japanese army were not limited to that period. Many atrocities were reported to have been committed as the Japanese army advanced from Shanghai to Nanking.
According to one Japanese journalist embedded with Imperial forces at the time:[15]
The reason that the [10th Army] is advancing to Nanking quite rapidly is due to the tacit consent among the officers and men that they could loot and rape as they wish.
In his novel Ikiteiru Heitai ('Living Soldiers'), Tatsuzō Ishikawa vividly describes how the 16th Division of the Shanghai Expeditionary Force committed atrocities on the march between Shanghai and Nanking. The novel itself was based on interviews that Ishikawa conducted with troops in Nanking in January 1938.[16]
Perhaps the most notorious atrocity was a killing contest between two Japanese officers as reported in the Tokyo Nichi Nichi Shimbun and the English-language Japan Advertiser. The contest—a race between the two officers to see who could kill 100 people first using only a sword—was covered much like a sporting event with regular updates on the score over a series of days.[17][18] In Japan, the veracity of the newspaper article about the contest was the subject of ferocious debate for several decades starting in 1967.[19]
In 2000, historian Bob Tadashi Wakabayashi concurred with certain Japanese scholars who had argued that the contest was a concocted story, with the collusion of the soldiers themselves for the purpose of raising the national fighting spirit.[20]
In 2005, a Tokyo district judge dismissed a suit by the families of the lieutenants, stating that "the lieutenants admitted the fact that they raced to kill 100 people" and that the story cannot be proven to be clearly false.[21] The judge also ruled against the civil claim of the plaintiffs because the original article was more than 60 years old.[22] The historicity of the event remains disputed in Japan.[23]
Retreating Chinese Troops' Scorched-Earth Policy
The Nanking garrison force set fire to buildings and houses in the areas close to Xiakuan to the north as well as in the environs of the eastern and southern city gates. Targets within and outside of the city walls—such as military barracks, private homes, the Chinese Ministry of Communication, forests and even entire villages—were completely burnt down, at an estimated value of US$20–30 million (1937).[24][25][26]
Establishment of the Nanking Safety Zone
Many Westerners were living in the city at that time, conducting trade or on missionary trips. As the Japanese army approached Nanking, most of them fled the city, leaving 27 foreigners. Five of these were journalists who remained in the city a few days after it was captured, leaving the city on December 16. Fifteen of the remaining 22 foreigners formed a committee, called the International Committee for the Nanking Safety Zone in the western quarter of the city.[27]
German businessman John Rabe was elected as its leader, in part because of his status as a member of the Nazi Party and the existence of the German-Japanese bilateral Anti-Comintern Pact. The Japanese government had previously agreed not to attack parts of the city that did not contain Chinese military forces, and the members of the Committee managed to persuade the Chinese government to move their troops out of the area. The Nanking Safety Zone was demarcated through the use of Red Cross Flags.[28]
On December 1, 1937, Nanking Mayor Ma Chaochun ordered all Chinese citizens remaining in Nanking to move into the "Safety Zone." Many fled the city on December 7, and the International Committee took over as the de facto government of Nanking.
Prince Asaka appointed as commander

In a memorandum for the palace rolls, Hirohito singled Prince Yasuhiko Asaka out for censure as the one imperial kinsman whose attitude was "not good." He assigned Asaka to Nanking as an opportunity to make amends.[29]
On December 5, Asaka left Tokyo by plane and arrived at the front three days later. He met with division commanders, lieutenant-generals Kesago Nakajima and Heisuke Yanagawa, who informed him that the Japanese troops had almost completely surrounded 300,000 Chinese troops in the vicinity of Nanking and that preliminary negotiations suggested that the Chinese were ready to surrender.[30]
Prince Asaka issued an order to "kill all captives," thus providing official sanction for the crimes which took place during and after the battle.[31] Some authors record that Prince Asaka signed the order for Japanese soldiers in Nanking to "kill all captives".[32] Others assert that lieutenant colonel Isamu Chō, Asaka's aide-de-camp, sent this order under the Prince's sign-manual without the Prince's knowledge or assent.[33] Nevertheless, even if Chō took the initiative, Asaka was nominally the officer in charge and gave no orders to stop the carnage. While the extent of Prince Asaka's responsibility for the massacre remains a matter of debate, the ultimate sanction for the massacre and the crimes committed during the invasion of China were issued in Emperor Hirohito's ratification of the Japanese army's proposition to remove the constraints of international law on the treatment of Chinese prisoners on August 5, 1937.[34]
Battle of Nanking
Siege of the city
The Japanese military continued to move forward, breaching the last lines of Chinese resistance, and arriving outside the city gates of Nanking on December 9.
Demand for surrender
At noon on December 9, the Japanese military dropped leaflets into the city, urging the city of Nanking to surrender within 24 hours, promising "no mercy" if the offer was refused.[35][note 2]
In the meantime, members of the Committee contacted Tang and proposed a plan for three-day cease-fire, during which the Chinese troops could withdraw without fighting while the Japanese troops would stay in their present position.
John Rabe boarded the U.S. gunboat Panay on December 9 and sent two telegrams, one to Chiang Kai-shek by way of the American ambassador in Hankow, and one to the Japanese military authority in Shanghai.
Assault and capture of Nanking

The Japanese awaited an answer to their demand for surrender but no response was received from the Chinese by the deadline on December 10. General Iwane Matsui waited another hour before issuing the command to take Nanking by force. The Japanese army mounted its assault on the Nanking walls from multiple directions; the SEF's 16th Division attacked three gates on the eastern side, the 6th Division of the 10A launched its offensive on the western walls, and the SEF's 9th Division advanced into the area in-between.[12]
On December 12, under heavy artillery fire and aerial bombardment, General Tang Sheng-chi ordered his men to retreat. What followed was nothing short of chaos. Some Chinese soldiers stripped civilians of their clothing in a desperate attempt to blend in, and many others were shot by the Chinese supervisory unit as they tried to flee.[24]
On 13 December, the 6th and the 116th Divisions of the Japanese Army were the first to enter the city, facing little military resistance. Simultaneously, the 9th Division entered nearby Guanghua Gate, and the 16th Division entered the Zhongshan and Taiping gates. That same afternoon, two small Japanese Navy fleets arrived on both sides of the Yangtze River.
Pursuit and mopping-up operations
Japanese troops pursued the retreating Chinese army units, primarily in the Xiakuan area to the north of the city walls and around the Zijin Mountain in the east. Although most sources suggest that the final phase of the battle consisted of a one-sided slaughter of Chinese troops by the Japanese, some Japanese historians maintain that the remaining Chinese military still posed a serious threat to the Japanese. Prince Yasuhiko Asaka told a war correspondent later that he was in a very perilous position when his headquarters was ambushed by Chinese forces that were in the midst of fleeing from Nanking east of the city. On the other side of the city, the 11th Company of the 45th Regiment encountered some 20,000 Chinese soldiers who were making their way from Xiakuan.[12]
The Japanese army conducted its mopping-up operation both inside and outside the Nanking Safety Zone. Since the area outside the safety zone had been almost completely evacuated, the mopping-up effort was concentrated in the safety zone. The safety zone, an area of 3.85 square kilometres, was packed with the remaining population of Nanking. The Japanese army leadership assigned sections of the safety zone to some units to separate alleged plain-clothed soldiers from the civilians.[12] The number of Chinese soldiers in plain clothes that were executed is estimated to be around 4,000.[36]
Civilian evacuation
Evacuation and flight of civilians
With the relocation of the capital of China and the reports of Japanese brutality, most of the civilian population fled Nanking out of fear. Wealthy families were the first to flee, leaving Nanking in automobiles, followed by the evacuation of the middle class and then the poor, while only the destitute lowest class such as the ethnic Tanka boat people remained behind.[37]
More than three quarters of the population had fled Nanking before the Japanese arrived.[38]
Massacre
| Nanjing Massacre | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chinese name | |||||||||
| Traditional Chinese | 南京大屠殺 | ||||||||
| Simplified Chinese | 南京大屠杀 | ||||||||
| |||||||||
| Japanese name | |||||||||
| Kanji | 1. 南京大虐殺 2. 南京事件 | ||||||||
| |||||||||
From December 13, 1937, the Japanese Army engaged in random murder, wartime rape, looting, arson, and other war crimes. Such crime continued from three to six weeks depending on the types of crime. The first three weeks were more intense.[note 1] A group of foreign expatriates headed by Rabe had formed a 15-man International Committee for the Nanking Safety Zone on November 22 and mapped out the Nanking Safety Zone in order to safeguard civilians in the city.[40]
Massacre contest
In 1937, the Osaka Mainichi Shimbun and its sister newspaper, the Tokyo Nichi Nichi Shimbun, covered a contest between two Japanese officers, Toshiaki Mukai and Tsuyoshi Noda of the Japanese 16th Division. The two men were described as vying to be the first to kill 100 people with a sword before the capture of Nanking. From Jurong to Tangshan (two cities in Jiangshu Province, China), Mukai had killed 89 people while Noda had killed 78. The contest continued because neither had killed 100 people. By the time they had arrived at Zijin Mountain, Noda had killed 105 people while Mukai had killed 106 people. Both officers supposedly surpassed their goal during the heat of battle, making it impossible to determine which officer had actually won the contest. Therefore, according to journalists Asami Kazuo and Suzuki Jiro, writing in the Tokyo Nichi Nichi Shimbun of December 13, they decided to begin another contest to kill 150 people.[41] After the surrender of Japan in 1945, Mukai and Noda were both arrested and tried as war criminals, and both of them were found guilty and executed by shooting on 28 January 1948.[42]
Evidence collection
The Japanese either destroyed or concealed important documents, severely reducing the amount of evidence available for confiscation. Between the declaration of a ceasefire on August 15, 1945, and the arrival of American troops in Japan on August 28, "the Japanese military and civil authorities systematically destroyed military, naval, and government archives, much of which was from the period 1942–1945."[43] Overseas troops in the Pacific and East Asia were ordered to destroy incriminating evidence of war crimes.[43] Approximately 70 percent of the Japanese army's wartime records were destroyed. [43] In regards to the Nanking Massacre, Japanese authorities deliberately concealed wartime records, eluding confiscation from American authorities.[44] Some of the concealed information was made public a few decades later. For example, a two-volume collection of military documents related to the Nanking operations was published in 1989; and disturbing excerpts from Kesago Nakajima's diary, a commander at Nanking, was published in the early 1980s.[44]
Ono Kenji, a chemical worker in Japan, began to curate a collection of wartime diaries from Japanese veterans who fought in the battle of Nanking in 1937.[45] In 1994, nearly 20 diaries in his collection were published, which became an important source of evidence for the massacre. Official war journals and diaries were also published by Kaikosha, an organization of retired Japanese military veterans.[46]
In early 1980s, after interviewing Chinese survivors and reviewing Japanese records, Japanese journalist Honda Katsuichi claimed that the Nanking Massacre was not an isolated case, and that Japanese atrocities against the Chinese were common throughout the Lower Yangtze River since the battle of Shanghai.[47] His claims have been corroborated with the diaries of other medics and combatants who fought in China.[48]
Rape
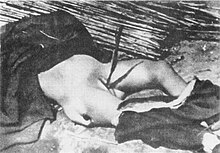

The International Military Tribunal for the Far East estimated that 20,000 women, including some children and the elderly, were raped during the occupation, with Yale University claiming over 80,000 rapes.[4][51] A large number of rapes were done systematically by the Japanese soldiers as they went from door to door, searching for girls, with many women being captured and gang-raped.[52] The women were often killed immediately after being raped, often through explicit mutilation,[53] such as by penetrating vaginas with bayonets, long sticks of bamboo, or other objects.
On 19 December 1937, the Reverend James M. McCallum wrote in his diary:[54]
I know not where to end. Never I have heard or read such brutality. Rape! Rape! Rape! We estimate at least 1,000 cases a night and many by day. In case of resistance or anything that seems like disapproval, there is a bayonet stab or a bullet.... People are hysterical... Women are being carried off every morning, afternoon and evening. The whole Japanese army seems to be free to go and come as it pleases, and to do whatever it pleases.
On March 7, 1938, Robert O. Wilson, a surgeon at the university hospital in the Safety Zone administrated by the United States, wrote in a letter to his family, "a conservative estimate of people slaughtered in cold blood is somewhere about 100,000, including of course thousands of soldiers that had thrown down their arms."[55] Here are two excerpts from his letters of 15 and 18 December 1937 to his family:[56]
The slaughter of civilians is appalling. I could go on for pages telling of cases of rape and brutality almost beyond belief. Two bayoneted corpses are the only survivors of seven street cleaners who were sitting in their headquarters when Japanese soldiers came in without warning or reason and killed five of their number and wounded the two that found their way to the hospital. Let me recount some instances occurring in the last two days. Last night the house of one of the Chinese staff members of the university was broken into and two of the women, his relatives, were raped. Two girls, about 16, were raped to death in one of the refugee camps. In the University Middle School where there are 8,000 people the Japs came in ten times last night, over the wall, stole food, clothing, and raped until they were satisfied. They bayoneted one little boy of eight who [had] five bayonet wounds including one that penetrated his stomach, a portion of omentum was outside the abdomen. I think he will live.
In his diary kept during the aggression against the city and its occupation by the Imperial Japanese Army, the leader of the Safety Zone, John Rabe, wrote many comments about Japanese atrocities. For 17 December:[57]
Two Japanese soldiers have climbed over the garden wall and are about to break into our house. When I appear they give the excuse that they saw two Chinese soldiers climb over the wall. When I show them my party badge, they return the same way. In one of the houses in the narrow street behind my garden wall, a woman was raped, and then wounded in the neck with a bayonet. I managed to get an ambulance so we can take her to Kulou Hospital ... Last night up to 1,000 women and girls are said to have been raped, about 100 girls at Ginling College...alone. You hear nothing but rape. If husbands or brothers intervene, they're shot. What you hear and see on all sides is the brutality and bestiality of the Japanese soldiers.
In a documentary film about the Nanking Massacre, In the Name of the Emperor, a former Japanese soldier named Shiro Azuma spoke candidly about the process of rape and murder in Nanking.[58]
At first we used some kinky words like Pikankan. Pi means "hip," kankan means "look." Pikankan means, "Let's see a woman open up her legs." Chinese women didn't wear under-pants. Instead, they wore trousers tied with a string. There was no belt. As we pulled the string, the buttocks were exposed. We "pikankan." We looked. After a while we would say something like, "It's my day to take a bath," and we took turns raping them. It would be all right if we only raped them. I shouldn't say all right. But we always stabbed and killed them. Because dead bodies don't talk.
Iris Chang, author of the Rape of Nanking (book), wrote one of the most comprehensive accounts of Japanese war atrocities in China.[59] In her book, she estimated that the number of Chinese women raped by Japanese soldiers ranged from 20,000 to 80,000. Chang also states that not all rape victims were women. Some Chinese men were sodomized and forced to perform "repulsive sex acts".[60][61] There are also accounts of Japanese troops coercing families to commit incestuous acts.[62] Sons were coerced in to rape their mothers, fathers were forced to rape their daughters, and brothers were forced to rape their sisters. Instead of punishing the Japanese troops who were responsible for wholesale rape, "'The Japanese expeditionary Force in Central China issued an order to set up comfort houses during this period of time,' Yoshimi Yoshiaki, a prominent history professor at Chuo University, observes, 'because Japan was afraid of criticism from China, the United States of America and Europe following the case of massive rapes between battles in Shanghai and Nanking.'"[63]
Massacre of civilians
For about three weeks since December 13, 1937,[1] the Imperial Japanese Army entered the Nanking Safety Zone to search for former Chinese soldiers hidden among refugees. Many innocent men were misidentified and killed.[1]
The death toll of civilians is difficult to precisely calculate due to the many bodies deliberately burnt, buried in mass graves, or dumped into the Yangtze River.[64][65] Robert O. Wilson, a physician, testified that cases of gun wounds "continued to come in [to the hospital of University of Nanking] for a matter of some six or seven weeks following the fall of the city on December 13, 1937. The capacity of the hospital was normally one hundred and eighty beds, and this was kept full to overflowing during this entire period.[66] B. Campbell described the Nanking Massacre as a genocide, given the fact that residents were still slaughtered en masse during the aftermath, despite the successful and certain outcome in battle.[67] However, Jean-Louis Margolin does not believe that the Nanking atrocities should be considered a genocide because only prisoners of war were executed in a systematic manner and the targeting of civilians was sporadic and done without orders by individual actors.[68] On 13 December 1937, John Rabe wrote in his diary:
It is not until we tour the city that we learn the extent of destruction. We come across corpses every 100 to 200 yards. The bodies of civilians that I examined had bullet holes in their backs. These people had presumably been fleeing and were shot from behind. The Japanese march through the city in groups of ten to twenty soldiers and loot the shops.... I watched with my own eyes as they looted the café of our German baker Herr Kiessling. Hempel's hotel was broken into as well, as [was] almost every shop on Chung Shang and Taiping Road.[69]
On 10 February 1938, Legation Secretary of the German Embassy, Rosen, wrote to his Foreign Ministry about a film made in December by Reverend John Magee to recommend its purchase.
During the Japanese reign of terror in Nanking—which, by the way, continues to this day to a considerable degree—the Reverend John Magee, a member of the American Episcopal Church Mission who has been here for almost a quarter of a century, took motion pictures that eloquently bear witness to the atrocities committed by the Japanese.... One will have to wait and see whether the highest officers in the Japanese army succeed, as they have indicated, in stopping the activities of their troops, which continue even today.[69] On December 13, about 30 soldiers came to a Chinese house at No. 5 Hsing Lu Koo in the southeastern part of Nanking and demanded entrance. The door was open by the landlord, a Mohammedan named Ha. They killed him immediately with a revolver and also Mrs. Ha, who knelt before them after Ha's death, begging them not to kill anyone else. Mrs. Ha asked them why they killed her husband and they shot her. Mrs. Hsia was dragged out from under a table in the guest hall where she had tried to hide with her 1-year-old baby. After being stripped and raped by one or more men, she was bayoneted in the chest and then had a bottle thrust into her vagina. The baby was killed with a bayonet. Some soldiers then went to the next room, where Mrs. Hsia's parents, aged 76 and 74, and her two daughters aged 16 and 14 [were]. They were about to rape the girls when the grandmother tried to protect them. The soldiers killed her with a revolver. The grandfather grasped the body of his wife and was killed. The two girls were then stripped, the elder being raped by 2–3 men and the younger by 3. The older girl was stabbed afterwards and a cane was rammed in her vagina. The younger girl was bayoneted also but was spared the horrible treatment that had been meted out to her sister and mother. The soldiers then bayoneted another sister of between 7–8, who was also in the room. The last murders in the house were of Ha's two children, aged 4 and 2 respectively. The older was bayoneted and the younger split down through the head with a sword.[69]
On 5 February 2009, the Japanese Supreme Court ordered Shūdō Higashinakano and the publisher Tendensha to pay four million yen in damages to Mrs. Shuqin Xia, who claims to be the 7- or 8-year-old girl who appears in Magee's film. Higashinakano had claimed in his book, Thorough Review of Nanking Massacre, that she and the girl were different persons, and that she was not a witness of the Nanking massacre, but he was unable to prove this at trial.[70]
Pregnant women were targeted for murder, as their stomachs were often bayoneted, sometimes after rape. Tang Junshan, survivor and witness to one of the Japanese army's systematic mass killings, testified:[71]
The seventh and last person in the first row was a pregnant woman. The soldier thought he might as well rape her before killing her, so he pulled her out of the group to a spot about ten meters away. As he was trying to rape her, the woman resisted fiercely.... The soldier abruptly stabbed her in the belly with a bayonet. She gave a final scream as her intestines spilled out. Then the soldier stabbed the fetus, with its umbilical cord clearly visible, and tossed it aside.
According to Navy veteran Sho Mitani, "The Army used a trumpet sound that meant 'Kill all Chinese who run away'."[72] Thousands were led away and mass-executed in an excavation known as the "Ten-Thousand-Corpse Ditch", a trench measuring about 300 m long and 5 m wide. Since records were not kept, estimates regarding the number of victims buried in the ditch range from 4,000 to 20,000. However, most scholars and historians consider the number to be more than 12,000 victims.[73]
The Hui people, a minority Chinese group, the majority of them Muslim, suffered as well during the massacre. One mosque was found destroyed and others found to be "filled with dead bodies." Hui volunteers and imams buried over a hundred of their dead following Muslim ritual.[74]
Extrajudicial killing of Chinese prisoners of war

Soon after the fall of the city, Japanese troops made a thorough search for Chinese soldiers and summarily arrested thousands of young Chinese men. Many were taken to the Yangtze River, where they were machine-gunned to death. What was probably the single largest massacre of Chinese troops, the Straw String Gorge Massacre, occurred along the banks of the Yangtze River on December 18. For most of the morning, Japanese soldiers tied the POWs' hands together. At dusk, the soldiers divided POWs into four columns and opened fire. Unable to escape, the POWs could only scream and thrash desperately. It took an hour for the sounds of death to stop and even longer for the Japanese to bayonet each individual. The majority of the bodies were dumped directly into the Yangtze River.[75]
Japanese troops gathered 1,300 Chinese soldiers and civilians at Taiping Gate and murdered them. The victims were blown up with landmines, then doused with petrol and set on fire. The survivors were killed with bayonets.[76]
U.S. news correspondents F. Tillman Durdin and Archibald Steele reported seeing corpses of massacred Chinese soldiers forming mounds six feet high at the Nanking Yijiang gate in the north. Durdin, who worked for The New York Times, toured Nanking before his departure from the city. He heard waves of machine-gun fire and witnessed the Japanese soldiers gun down some two hundred Chinese within ten minutes. He would later state that he had seen tank guns used on bound soldiers.
Two days later, in his report to The New York Times, Durdin stated that the alleys and streets were filled with the dead, amongst them women and children. Durdin stated "[i]t should be said that certain Japanese units exercised restraint and that certain Japanese officers tempered power with generosity and commission," but continued "the conduct of the Japanese army as a whole in Nanking was a blot on the reputation of their country"."[77][78]
Ralph L. Phillips, a missionary, testified to the U.S. State Assembly Investigating Committee, that he was "forced to watch while the Japs disembowled a Chinese soldier" and "roasted his heart and liver and ate them."[79]
Looting and arson
"In the first days of the occupation the soldiers [...] took a great deal of bedding, cooking utensils and food from the refugees. Practically every building in the city was entered many, many times by these roving gangs of soldiers throughout the first six or seven weeks of the occupation".[1] "[T]here was no burning until the Japanese troops had been in the city five or six days. Beginning, I believe, on the 19th or 20th of December, burning was carried on regularly for six weeks."[1]
One-third of the city was destroyed as a result of arson. According to reports, Japanese troops torched newly built government buildings as well as the homes of many civilians. There was considerable destruction to areas outside the city walls. Soldiers pillaged from the poor and the wealthy alike. The lack of resistance from Chinese troops and civilians in Nanking meant that the Japanese soldiers were free to divide up the city's valuables as they saw fit. This resulted in widespread looting and burglary.[80]
On 17 December, chairman John Rabe wrote a complaint to Kiyoshi Fukui, second secretary of the Japanese Embassy. The following is an excerpt:
In other words, on the 13th when your troops entered the city, we had nearly all the civilian population gathered in a Zone in which there had been very little destruction by stray shells and no looting by Chinese soldiers even in full retreat.... All 27 Occidentals in the city at that time and our Chinese population were totally surprised by the reign of robbery, raping and killing initiated by your soldiers on the 14th. All we are asking in our protest is that you restore order among your troops and get the normal city life going as soon as possible. In the latter process we are glad to cooperate in any way we can. But even last night between 8 and 9 p.m. when five Occidental members of our staff and Committee toured the Zone to observe conditions, we did not find any single Japanese patrol either in the Zone or at the entrances![81]
Nanking Safety Zone and the role of foreigners
The Japanese troops did respect the Zone to an extent; until the Japanese occupation, no shells entered that part of the city except a few stray shots. During the chaos following the attack of the city, some were killed in the Safety Zone, but the crimes that occurred in the rest of the city were far greater by all accounts.[82]
Rabe wrote that, from time to time, the Japanese would enter the Safety Zone at will, carry off a few hundred men and women, and either summarily execute them or rape and then kill them.[83]
By February 5, 1938, the International Committee for the Nanking Safety Zone had forwarded to the Japanese embassy a total of 450 cases of murder, rape, and general disorder by Japanese soldiers that had been reported after the American, British and German diplomats had returned to their embassies:[84]
- "Case 5 – On the night of December 14th, there were many cases of Japanese soldiers entering houses and raping women or taking them away. This created panic in the area and hundreds of women moved into the Ginling College campus yesterday."
- "Case 10 – On the night of December 15th, a number of Japanese soldiers entered the University of Nanking buildings at Tao Yuen and raped 30 women on the spot, some by six men."
- "Case 13 – December 18, 4 p.m., at No. 18 I Ho Lu, Japanese soldiers wanted a man's cigarette case and when he hesitated, one of the soldier crashed in the side of his head with a bayonet. The man is now at the University Hospital and is not expected to live."
- "Case 14 – On December 16, seven girls (ages ranged from 16 to 21) were taken away from the Military College. Five returned. Each girl was raped six or seven times daily – reported December 18th."
- "Case 15 – There are about 540 refugees crowded in No. 83 and 85 on Canton Road.... More than 30 women and girls have been raped. The women and children are crying all nights. Conditions inside the compound are worse than we can describe. Please give us help."
- "Case 16 – A Chinese girl named Loh, who, with her mother and brother, was living in one of the Refugee Centers in the Refugee Zone, was shot through the head and killed by a Japanese soldier. The girl was 14 years old. The incident occurred near the Kuling Ssu, a noted temple on the border of the Refugee zone ..."[84]
- "Case 19 – January 30th, about 5 p.m. Mr. Sone (of the Nanking Theological Seminary) was greeted by several hundred women pleading with him that they would not have to go home on February 4th. They said it was no use going home they might just as well be killed for staying at the camp as to be raped, robbed or killed at home.... One old woman 62 years old went home near Hansimen and Japanese soldiers came at night and wanted to rape her. She said she was too old. So the soldiers rammed a stick up her. But she survived to come back."
It is said that Rabe rescued between 200,000 and 250,000 Chinese people.[85][86]
Causes
Jonathan Spence writes:[87]
[T]here is no obvious explanation for this grim event, nor can one be found. The Japanese soldiers, who had expected easy victory, instead had been fighting hard for months and had taken infinitely higher casualties than anticipated. They were bored, angry, frustrated, tired. The Chinese women were undefended, their menfolk powerless or absent. The war, still undeclared, had no clear-cut goal or purpose. Perhaps all Chinese, regardless of sex or age, seemed marked out as victims.
Photo in the album taken in Nanjing by Itou Kaneo of the Kisarazu Air Unit of the Imperial Japanese Navy
A picture of a dead child. Probably taken by Bernhard Sindberg
Prisoners being buried alive[88]
Skeletons of the massacre's victims
The dehumanization of Chinese people in the Japanese education system is also blamed for why many ordinary soldiers were eager to engage in atrocities.[89]
Literature
Eyewitness accounts include testimonies of expatriates engaged in humanitarian work (mostly physicians, professors, missionary and businessmen), journalists (both Western and Japanese), as well as the field diaries of military personnel. American missionary John Magee stayed behind to provide a 16 mm film documentary and first-hand photographs of the Nanking Massacre. Rabe and American missionary Lewis S. C. Smythe, secretary of the International Committee and a professor of sociology at the University of Nanking, recorded the actions of the Japanese troops and filed complaints with the Japanese embassy.
Matsui's reaction to the massacre
On December 18, 1937, as General Iwane Matsui began to comprehend the full extent of the rape, murder, and looting in the city, he grew increasingly dismayed. He reportedly told one of his civilian aides:
I now realize that we have unknowingly wrought a most grievous effect on this city. When I think of the feelings and sentiments of many of my Chinese friends who have fled from Nanking and of the future of the two countries, I cannot but feel depressed. I am very lonely and can never get in a mood to rejoice about this victory.... I personally feel sorry for the tragedies to the people, but the Army must continue unless China repents. Now, in the winter, the season gives time to reflect. I offer my sympathy, with deep emotion, to a million innocent people.
On New Year's Day, over a toast he confided to a Japanese diplomat: "My men have done something very wrong and extremely regrettable."[90] Matsui blamed the atrocities on the moral decline of the Japanese Army, saying:
The Nanking Incident was a terrible disgrace ... Immediately after the memorial services, I assembled the higher officers and wept tears of anger before them, as Commander-in-Chief ... I told them that after all our efforts to enhance the Imperial prestige, everything had been lost in one moment through the brutalities of the soldiers. And can you imagine it, even after that, these officers laughed at me ... I am really, therefore, quite happy that I, at least, should have ended this way, in the sense that it may serve to urge self-reflection on many more members of the military of that time.[91]
End of the massacre
In late January 1938, the Japanese army forced all refugees in the Safety Zone to return home, immediately claiming to have "restored order". After the establishment of the weixin zhengfu (the collaborating government) in 1938, order was gradually restored in Nanking and atrocities by Japanese troops lessened considerably.[citation needed]
On 18 February 1938, the International Committee for the Nanking Safety Zone was forcibly renamed the Nanking International Rescue Committee, and the Safety Zone effectively ceased to function. The last refugee camps were closed in May 1938.[citation needed]
Recall of Matsui and Asaka
In February 1938, both Prince Asaka and General Matsui were recalled to Japan. Matsui returned to retirement, but Prince Asaka remained on the Supreme War Council until the end of the war in August 1945. He was promoted to the rank of general in August 1939, though he held no further military commands.[31]
Death toll estimates

Numerous factors complicate the estimation of an accurate death toll.[92][93]
According to American historian Edward J. Drea:
While the Germans, beginning in 1943, did engage in substantial efforts to obliterate evidence of such crimes as mass murder, and they destroyed a great deal of potentially incriminating records in 1945, a great deal survived, in part because not each one of the multiple copies had been burned. The situation was different in Japan. Between the announcement of a ceasefire on August 15, 1945, and the arrival of small advance parties of American troops in Japan on August 28, Japanese military and civil authorities systematically destroyed military, naval, and government archives, much of which was from the period 1942–1945.Imperial General Headquarters in Tokyo dispatched enciphered messages to field commands throughout the Pacific and East Asia ordering units to burn incriminating evidence of war crimes, especially offenses against prisoners of war.[92]
According to Yang Daqing, professor of History and International Affairs at George Washington University:
While it is standard practice for governments to destroy evidence in times of defeat, in the two weeks before the Allies arrived in Japan, various Japanese agencies—the military in particular—systematically destroyed sensitive documents to a degree perhaps unprecedented in history. Estimates of the impact of the destruction vary. Tanaka Hiromi, a professor at Japan’s National Defense Academy who has conducted extensive research into remaining Imperial Japanese Army and Navy documents in Japan and overseas, claims that less than 0.1 percent of the material ordered for destruction survived.[94]
In 2003, the director of Japan's Military History Archives of National Institute for Defense Studies said that as much 70 percent of Japan's wartime records were destroyed.[92]
Other factors include the mass disposal of Chinese corpses by Japanese soldiers; the revisionist tendencies of both Chinese and Japanese individuals and groups, who are driven by nationalistic and political motivations; and the subjectivity involved in the collection and interpretation of evidence.[4][8][93][95] However, the most credible scholars in Japan, which include a large number of authoritative academics, support the validity of the International Military Tribunal for the Far East and its findings, which estimate at least 200,000 casualties and at least 20,000 cases of rape.[8][9]
Historian Tokushi Kasahara states "more than 100,000 and close to 200,000, or maybe more."[96] With the emergence of more information and data, he said that there is a possibility that the death toll could be higher. Hiroshi Yoshida concludes "more than 200,000" in his book.[97] Tomio Hora supports the information found in the International Military Tribunal for the Far East, which estimates a death toll of at least 200,000.[98][99] An estimate death toll of 300,000 has also been cited.[64]
According to the International Military Tribunal for the Far East, estimates made at a later date indicate that the total number of civilians and prisoners of war murdered in Nanking and its vicinity during the first six weeks of the Japanese occupation was over 200,000. These estimates are borne out by the figures of burial societies and other organizations, which testify to over 155,000 buried bodies. These figures also do not take into account those persons whose bodies were destroyed by burning, drowning or other means, or whose bodies were interred in mass graves.[65] The most credible scholars in Japan, which include a large number of authoritative academics, support the validity of the tribunal and its findings.[8]
According to the verdict of the Nanking War Crimes Tribunal on 10 March 1947, there are "more than 190,000 mass slaughtered civilians and Chinese soldiers killed by machine gun by the Japanese army, whose corpses have been burned to destroy proof. Besides, we count more than 150,000 victims of barbarian acts buried by the charity organizations. We thus have a total of more than 300,000 victims."[100] However, this estimate includes an accusation that the Japanese Army murdered 57,418 Chinese POWs at Mufushan, though the latest research indicates that between 4,000 and 20,000 were massacred,[101][102] and it also includes the 112,266 corpses allegedly buried by the Chongshantang, a charitable association, though today mainstream historians agree that the Chongshantang's records were at least greatly exaggerated if not entirely fabricated.[103][104][105] According to Bob Wakabayashi, he estimates the death toll within Nanking City Wall to be around 40,000, mostly massacred in the first five days; while the total victims after a 3-month period in Nanking and its surrounding six rural counties "far exceed 100,000 but fall short of 200,000".[8] Wakabayashi concludes that estimates of over 200,000 are not credible.[104]
John Rabe, Chairman of the International Committee for the Nanking Safety Zone, estimated that between 50,000 and 60,000 (civilians) were killed.[106] However, Erwin Wickert, the editor of The diaries of John Rabe, points out that "It is likely that Rabe's estimate is too low, since he could not have had an overview of the entire municipal area during the period of the worst atrocities. Moreover, many troops of captured Chinese soldiers were led out of the city and down to the Yangtze, where they were summarily executed. But, as noted, no one actually counted the dead."

Harold Timperley, a journalist in China during the Japanese invasion, reported that at least 300,000 Chinese civilians were killed in Nanking and elsewhere, and tried to send a telegram but was censored by the Japanese military in Shanghai.[106] Other sources, including Iris Chang's The Rape of Nanking, also conclude that the death toll reached 300,000. In December 2007, newly declassified U.S. government archive documents revealed that a telegraph by the U.S. ambassador to Germany in Berlin sent one day after the Japanese army occupied Nanking, stated that he heard the Japanese ambassador in Germany boasting that the Japanese army had killed 500,000 Chinese soldiers and civilians as the Japanese army advanced from Shanghai to Nanking. According to the archives research "The telegrams sent by the U.S. diplomats [in Berlin] pointed to the massacre of an estimated half a million people in Shanghai, Suzhou, Jiaxing, Hangzhou, Shaoxing, Wuxi and Changzhou".[107][108]
In the 2010 Japan-China Joint History Research Committee meeting, scholars from the Japanese side set the maximum possible number of civilian victims at 200,000, with estimates of around 40,000 or 20,000. The Chinese scholars of the committee maintained that at least 300,000 were killed.[109]
Range and duration
The duration of the incident is naturally defined by its geography: the earlier the Japanese entered the area, the longer the duration. The Battle of Nanking ended on December 13, when the divisions of the Japanese Army entered the walled city of Nanking. The Tokyo War Crime Tribunal defined the period of the massacre to the ensuing six weeks. More conservative estimates say that the massacre started on December 14, when the troops entered the Safety Zone, and that it lasted for six weeks. Historians who define the Nanking Massacre as having started from the time that the Japanese Army entered Jiangsu province push the beginning of the massacre to around mid-November to early December (Suzhou fell on November 19), and extended the end of the massacre to late March 1938.[citation needed]
To many Japanese scholars, post-war estimations were distorted by "victor's justice", when Japan was condemned as the sole aggressor. They believed the 300,000 toll typified a "Chinese-style exaggeration" with disregard for evidence. Yet, in China, this figure has come to symbolize the justice, legality, and authority of the post-war trials condemning Japan as the aggressor.[110]
War crimes tribunals
Shortly after the surrender of Japan, the primary officers in charge of the Japanese troops at Nanking were put on trial. General Matsui was indicted before the International Military Tribunal for the Far East for "deliberately and recklessly" ignoring his legal duty "to take adequate steps to secure the observance and prevent breaches" of the Hague Convention. Hisao Tani, the lieutenant general of the 6th Division of the Imperial Japanese Army in Nanking, was tried by the Nanking War Crimes Tribunal.
Other Japanese military leaders in charge at the time of the Nanking Massacre were not tried. Prince Kan'in Kotohito, chief of staff of the Imperial Japanese Army during the massacre, had died before the end of the war in May 1945. Prince Asaka was granted immunity because of his status as a member of the imperial family.[111][112] Isamu Chō, the aide to Prince Asaka, and whom some historians believe issued the "kill all captives" memo, had committed suicide during the Battle of Okinawa.[113]
The International Military Tribunal for the Far East was convened at "Ichigaya Court," formally Imperial Japanese Army HQ building in Ichigaya, Tokyo.
General Iwane Matsui[114]
General Hisao Tani[115]
Grant of immunity to Prince Asaka
On May 1, 1946, SCAP officials interrogated Prince Asaka, who was the ranking officer in the city at the height of the atrocities, about his involvement in the Nanking Massacre and the deposition was submitted to the International Prosecution Section of the Tokyo tribunal. Asaka denied the existence of any massacre and claimed never to have received complaints about the conduct of his troops.[116]
Evidence and testimony

The prosecution began the Nanking phase of its case in July 1946. Dr. Robert O. Wilson, a surgeon and a member of the International Committee for the Nanking Safety Zone, took the witness stand first. Other members of the International Committee for the Nanking Safety Zone who took the witness stand included Miner Searle Bates and John Magee. George A. Fitch, Lewis S. C. Smythe, and James McCallum filed affidavits with their diaries and letters.
Another piece of evidence that was submitted to the tribunal was Harold Timperley's telegram regarding the Nanking Massacre which had been intercepted and decoded by the Americans on January 17, 1938. One of the books by Hsü, Documents of the Nanking Safety Zone, was also adduced in court.[citation needed]
The entry for the same day in Matsui's diary read, "I could only feel sadness and responsibility today, which has been overwhelmingly piercing my heart. This is caused by the Army's misbehaviors after the fall of Nanking and failure to proceed with the autonomous government and other political plans."[citation needed]
Matsui's defense
This section relies largely or entirely on a single source. (June 2016) |
Matsui asserted that he had never ordered the execution of Chinese POWs. He further argued that he had directed his army division commanders to discipline their troops for criminal acts, and was not responsible for their failure to carry out his directives. At trial, Matsui went out of his way to protect Prince Asaka by shifting blame to lower-ranking division commanders.[117]
Verdict
Kōki Hirota, who had been the Foreign Minister when Japan conquered Nanking, was convicted of participating in "the formulation or execution of a common plan or conspiracy" (count 1), waging "a war of aggression and a war in violation of international laws, treaties, agreements and assurances against the Republic of China" (count 27) and count 55. Matsui was convicted by a majority of the judges at the Tokyo tribunal who ruled that he bore ultimate responsibility for the "orgy of crime" at Nanking because, "He did nothing, or nothing effective, to abate these horrors."
Organized and wholesale murder of male civilians was conducted with the apparent sanction of the commanders on the pretext that Chinese soldiers had removed their uniforms and were mingling with the population. Groups of Chinese civilians were formed, bound with their hands behind their backs, and marched outside the walls of the city where they were killed in groups by machine gun fire and with bayonets. — From Judgment of the International Military Tribunal
Sentence
On November 12, 1948, Matsui and Hirota, along with five other convicted Class-A war criminals, were sentenced to death by hanging. Eighteen others received lesser sentences. The death sentence imposed on Hirota, a six-to-five decision by the eleven judges, shocked the general public and prompted a petition on his behalf, which soon gathered over 300,000 signatures but did not succeed in commuting the Minister's sentence. All of them were hanged on 23 December 1948[118][119]
General Hisao Tani was sentenced to death by the Nanking War Crimes Tribunal. He was executed in China on 26 April 1947.[117]
However, according to historian Tokushi Kasahara, the evidence used to convict Hisao Tani was not convincing.[120] Kasahara said that if there was a full investigation of the massacre, many other high ranking authorities, which include higher level commanders, army leaders and emperor Hirohito, could have been implicated.[120]
Memorials
- In 1985, the Nanking Massacre Memorial Hall was built by the Nanking Municipal Government in remembrance of the victims and to raise awareness of the Nanking Massacre. It is located near a site where thousands of bodies were buried, called the "pit of ten thousand corpses" (wàn rén kēng). As of December 2016[update], there is a total of 10,615 Nanking Massacre victim names inscribed on a memorial wall.[121]
- In 1995, Daniel Kwan held a photo exhibit in Los Angeles titled, "The Forgotten Holocaust".
- In 2005, John Rabe's former residence in Nanking was renovated and now accommodates the "John Rabe and International Safety Zone Memorial Hall", which opened in 2006.
- On December 13, 2009, both the Chinese and Japanese monks held a religious assembly to mourn Chinese civilians killed by invading Japanese troops.[122]
- On December 13, 2014, China held its first Nanking Massacre memorial day.[123]
On October 9, 2015, Documents of the Nanking Massacre have been listed on the UNESCO Memory of the World Register.[124]
Controversy
China and Japan have both acknowledged the occurrence of wartime atrocities.[125] Disputes over the historical portrayal of these events continue to cause tensions between Japan on one side and China and other East Asian countries on the other side.[126]
Cold War
Before the 1970s, China did relatively little to draw attention to the Nanking massacre. In her book Rape of Nanking, Iris Chang asserted that the politics of the Cold War encouraged Chairman Mao to stay relatively silent about Nanking in order to keep a trade relationship with Japan.[127] Jung Chang and Jon Halliday's biography of Mao claims Mao never made any comment either contemporaneously or later in his life about the massacre, but did frequently remark with enduring bitterness about a political struggle between himself and Wang Ming which also occurred in December 1937.[128]
Debate in Japan
The debate concerning the massacre took place mainly in the 1970s. During this time, the Chinese government's statements about the event were attacked by the Japanese because they were said to rely too heavily on personal testimonies and anecdotal evidence. Aspersions were cast regarding the authenticity and accuracy of burial records and photographs presented in the Tokyo War Crime Court, which the Japanese government claimed were fabrications by the Chinese government, artificially manipulated or incorrectly attributed to the Nanking Massacre.[129]
During the 1970s, Katsuichi Honda wrote a series of articles for the Asahi Shimbun on war crimes committed by Japanese soldiers during World War II (such as the Nanking Massacre).[130] The publication of these articles triggered a vehement response from Japanese right-wingers regarding the Japanese treatment of the war crimes. In response, Shichihei Yamamoto[131] and Akira Suzuki[132] wrote two controversial yet influential articles[clarification needed] which sparked the Japanese Negationist movement.[clarification needed]
In 1984, in an attempt to refute the allegations of war crimes in Nanking, the Japanese Army Veterans Association (Kaikosha) interviewed former Japanese soldiers who had served in the Nanking area from 1937 to 1938. Instead of refuting the allegations, the interviewed veterans confirmed that a massacre had taken place and openly described and admitted to taking part in the atrocities. The results of the survey were published in the association's magazine, Kaiko, in 1985 along with an admission and apology that read, "Whatever the severity of war or special circumstances of war psychology, we just lose words faced with this mass illegal killing. As those who are related to the prewar military, we simply apologize deeply to the people of China. It was truly a regrettable act of barbarity."[133]
Apology and condolences by the Prime Minister and Emperor of Japan
On August 15, 1995, the fiftieth anniversary of the Surrender of Japan, the Japanese prime minister Tomiichi Murayama gave the first formal apology for Japanese actions during the war.[134]
He offered his apology to all survivors and to the relatives and friends of the victims. That day, the prime minister and the Japanese Emperor Akihito pronounced statements of mourning at Tokyo's Nippon Budokan. Iris Chang, author of The Rape of Nanking, criticized Murayama for not providing the written apology that had been expected. She said that the people of China "don't believe that an... unequivocal and sincere apology has ever been made by Japan to China" and that a written apology from Japan would send a better message to the international community.[135]
Denials of the massacre by public officials in Japan
A faction of Japanese politicians who are unapologetic to the deaths in Nanking have triggered a recurring point of tension in Sino-Japanese relations.[136][137]
In May 1994, Justice Minister Shigeto Nagano called the Nanking Massacre a "fabrication".[138]
On June 19, 2007, a group of around 100 Liberal Democratic Party (LDP) lawmakers again denounced the Nanking Massacre as a fabrication, arguing that there was no evidence to prove the allegations of mass killings by Japanese soldiers. They accused Beijing of using the alleged incident as a "political advertisement".[139][140]
On February 20, 2012, Takashi Kawamura, mayor of Nagoya, told a visiting delegation from Nanking that the massacre "probably never happened". Two days later he defended his remarks, saying, "Even since I was a national Diet representative, I have said [repeatedly] there was no [Nanking] massacre that resulted in murders of several hundred thousands of people."[141][142]
On February 24, 2012, Tokyo governor Shintaro Ishihara denies the Nanking massacre. He alleged it would have been impossible to kill so many people in such a short period of time.[143] He alleges a death toll of 10,000.[144]
On February 3, 2014, Naoki Hyakuta, a member of the board of governors of Japan's public broadcasting company, NHK, was quoted as saying the massacre never occurred.[145] He said that there were isolated incidents of brutality but no widespread atrocity, and criticized the Tokyo Trials figure of 200,000.[146]
Legacy
Effect on international relations
The memory of the Nanking Massacre has been a point of contention in Sino-Japanese relations since the early 1970s.[147] Trade between the two nations is worth over $200 billion annually. Despite this, many Chinese people still have a strong sense of mistrust due to the memory of the atrocity and failure of reconciliation measures. This sense of mistrust is strengthened by Japan's unwillingness to admit to and apologize for the atrocities.[148]
Takashi Yoshida described how changing political concerns and perceptions of the "national interest" in Japan, China, and the U.S. have shaped the collective memory of the Nanking massacre. Yoshida contended that over time the event has acquired different meanings to different people. People from mainland China saw themselves as the victims. For Japan, it was a question they needed to answer but were reluctant to do so because they too identified themselves as victims after the A-bombs. The U.S., which served as the melting pot of cultures and is home to descendants of members of both Chinese and Japanese cultures, took up the mantle of investigator for the victimized Chinese. Yoshida has argued that the Nanking Massacre has figured in the attempts of all three nations as they work to preserve and redefine national and ethnic pride and identity, assuming different kinds of significance based on each country's changing internal and external enemies.[149]
Many Japanese prime ministers have visited the Yasukuni Shrine, a shrine for Japanese war deaths up until the end of the Second World War, which includes war criminals that were involved in the Nanking Massacre. In the museum adjacent to the shrine, a panel informs visitors that there was no massacre in Nanking, but that Chinese soldiers in plain clothes were "dealt with severely". In 2006 former Japanese prime minister Junichiro Koizumi made a pilgrimage to the shrine despite warnings from China and South Korea. His decision to visit the shrine regardless sparked international outrage. Although Koizumi denied that he was trying to glorify war or historical Japanese militarism, the Chinese Foreign Ministry accused Koizumi of "wrecking the political foundations of China-Japan relations". An official from South Korea said they would summon the Tokyo ambassador to protest.[150][151]
The Massacre is sometimes compared to other disasters in China, which include the Great Chinese famine (1959–61)[152][153][154] and the Cultural Revolution.[155][156][157]
As a component of national identity
Yoshida asserts that "Nanking has figured in the attempts of all three nations [China, Japan and the United States] to preserve and redefine national and ethnic pride and identity, assuming different kinds of significance based on each country's changing internal and external enemies."[158]
Japan
Following the end of World War II, some circles of civil society in Japan reflected on the extent of the massacre and the participation of ordinary soldiers. Notably, the novelist Hotta Yoshie wrote a novel, Time (Jikan) in 1953, portraying the massacre from the point of view of a Chinese intellectual watching it happen. This novel has been translated into Chinese and Russian. Other eyewitnesses to the massacre also expressed their opinions in Japanese magazines in the 1950s and 1960s, but political shifts slowly eroded this tide of confessions.
In 21st century Japan, the Nanking Massacre touches upon national identity and notions of "pride, honor and shame". Yoshida argues that "Nanking crystallizes a much larger conflict over what should constitute the ideal perception of the nation: Japan, as a nation, acknowledges its past and apologizes for its wartime wrongdoings; or ... stands firm against foreign pressures and teaches Japanese youth about the benevolent and courageous martyrs who fought a just war to save Asia from Western aggression."[159] Recognizing the Nanking Massacre as such can be viewed in some circles in Japan as "Japan-bashing" (in the case of foreigners) or "self-flagellation" (in the case of Japanese).[citation needed]
The government of Japan believes it can not be denied that the killing of a large number of noncombatants, looting and other acts by the Japanese army occurred. However, the actual number of victims is hard to determine, according to the government of Japan.[160] In the 2010 Japan-China Joint History Research Committee meeting, scholars from the Japanese side set the maximum possible number of civilian victims at 200,000, with estimates of around 40,000 or 20,000. The Chinese scholars of the committee maintained that at least 300,000 were killed.[109][161] The range of the death toll estimated by Japanese historians is from tens of thousands to 200,000.[162][163]
According to a brief reference to Nanking at the Yasukuni museum in Tokyo, the Japanese general in charge gave his men maps showing foreign settlements and a civilian "safety zone", and ordered them to maintain strict military discipline. The visitor is left to assume they did. The museum notes only that "Chinese soldiers disguised in civilian clothes, which numbered around 4000[36] were severely prosecuted".[citation needed]
This nationalist view does not, however, represent a widely shared understanding of what happened at Nanking, as illustrated by Japanese textbooks' rather different treatment of the atrocity. While the books' take on Nanking is stilted and feels like the product of a committee, in various versions they acknowledge the deaths of thousands of Chinese including women and children, as well as looting, arson and assaults by Japanese soldiers. They do not mention sexual assaults.[citation needed]
Some conspiracy theories claim that the whole event was entirely made up by the CCP and Chinese Nationalists as a weapon to attack Japan, deny the truth and facts of the war, and to indirectly justify China's discriminatory policies against minority groups in Xinjiang and Tibet.[164][165][166]
"During this period, when the Japanese Army occupied Nanking it killed a large number of Chinese and carried out looting, arson and assaults. In regard to the number of victims of this Nanking Massacre ... the Tokyo (War Crime) Trials later found it in excess of 200,000, and prosecuted Japan's responsibility severely", reads one Japanese textbook.[167]
Another history textbook prepared by the Japanese Society for History Textbook Reform, which had been approved by the government in 2001, attempts to whitewash Japan's war record during the 1930s and early 1940s. It referred to the Nanking massacre as an "incident", and glossed over the issue of comfort women.[168] Indeed, there is only one sentence that refers to this event: "they [the Japanese troops] occupied that city in December."[169]
China
The Nanking massacre has emerged as one fundamental keystone in the construction of the modern Chinese national identity.[170] Modern Chinese (including most citizens of the PRC, partially in Taiwan, Hong Kong, and overseas) will refer to the Nanking Massacre to explain certain stances they hold or ideas they have; this "national unifying event" holds true to middle-school educated peasants and to senior government officials alike.[citation needed]
The remembrance of the massacre has evolved drastically in China. Until 1982, mentioning of the massacre was suppressed in China because ideologically the communists would rather promote the "martyrs of class struggles" than wartime victims, especially when there were no communist heroes or any communists at all in Nanking when the massacre happened. Only since the 1990s, through the revisionist Patriotic Education Campaign, the massacre has become a national memory as an episode of the "Century of Humiliation" prior to the communist founding of a "New China". This orthodox victimhood narrative has become entwined with the Chinese national identity and is very sensitive to the revisionist sentiments from the far-right in Japan, which makes the memory of the massacre a recurring point of tension in Sino-Japanese relations after 1982.[171][172][173]
Australia
Dockworkers in Australia were horrified by the massacre and refused to load pig iron onto ships heading for Japan, leading to the Dalfram Dispute of 1938.[174]
Records
In December 2007, the PRC government published the names of 13,000 people who were killed by Japanese troops in the Nanking Massacre. According to Xinhua News Agency, it is the most complete record to date. The report consists of eight volumes and was released to mark the 70th anniversary of the start of the massacre. It also lists the Japanese army units that were responsible for each of the deaths and states the way in which the victims were killed. Zhang Xianwen, editor-in-chief of the report, states that the information collected was based on "a combination of Chinese, Japanese and Western raw materials, which is objective and just and is able to stand the trial of history".[175] This report formed part of a 55-volume series about the massacre, the Collection of Historical Materials of Nanking Massacre (南京大屠杀史料集).[citation needed]
See also
- 2005 anti-Japanese demonstrations
- Bataan Death March
- Burma Railway
- Changde chemical weapon attack
- Comfort women
- Finding Iris Chang
- Gando massacre
- Japanese Society for History Textbook Reform
- Jinan incident
- John Rabe
- Kaimingjie germ weapon attack
- Kantō Massacre
- List of massacres in China
- Zhejiang-Jiangxi campaign, resulted in approximately 250,000 Chinese civilian deaths due to Japanese war crimes including the use of biological weapons.
- Manila massacre
- Masanobu Tsuji
- Minnie Vautrin
- Red Swastika Society
- Shiro Azuma
- Sook Ching
- Three Alls Policy
- Unit 100
- Unit 731
Notes
- ^ a b c "Six weeks long" is a convenient figure but far from precise. Killings were most intense in the first five days from December 13 and remained moderately intense until December 31, 1937, according to the Japanese military records. From February 7, 1938, killings were no longer in mass fashion as the senior Japanese officers came to restore discipline of their troops, according to the testimony of Miner Searle Bates, a humanitarian leader of the Nanking Safety Zone. None of the above dates is close to "six weeks", which should correspond to January 24, 1938. Bates testified before the Tokyo Trial on July 29, 1946, pioneering the use of "six weeks long" and describing the respective duration of random murder, looting and arson.[1]
- ^ Quote: "The Japanese Army, one million strong, has already conquered Changshu. We have surrounded the city of Nanking... The Japanese Army shall show no mercy toward those who offer resistance, treating them with extreme severity, but shall harm neither innocent civilians nor Chinese military [personnel] who manifest no hostility. It is our earnest desire to preserve the East Asian culture. If your troops continue to fight, war in Nanking is inevitable. The culture that has endured for a millennium will be reduced to ashes, and the government that has lasted for a decade will vanish into thin air. This commander-in-chief issues [b]ills to your troops on behalf of the Japanese Army. Open the gates to Nanking in a peaceful manner, and obey the [f]ollowing instructions."
References
Citations
- ^ a b c d e Library of Congress, ed. (1964–1974). "29 July 1946. Prosecution's Witnesses. Bates, Miner Searle". Record of proceedings of the International Military Tribunal for the Far East. pp. 2631, 2635, 2636, 2642–2645.
- ^ According to the Wade-Giles Romanisation scheme commonly employed in documents of the period, the city's name is transliterated as "Nanking". However, using the Hanyu Pinyin system officially used by the PRC, the city's name would be transliterated as Nanjing.
- ^ a b "International Memory of the World Register Documents of Nanjing Massacre" (PDF). UNESCO. Retrieved 23 March 2022.
- ^ a b c "Nanking Massacre". Yale University. 17 January 1997. Retrieved 12 January 2022.
- ^ Chang, Iris. 1997. The Rape of Nanking. p. 6.
- ^ Lee, Min (March 31, 2010). "New film has Japan vets confessing to Nanjing rape". Salon/Associated Press.
- ^ Fogel, Joshua A. (2000). The Nanjing Massacre in History and Historiography. ISBN 9780520220072.
- ^ a b c d e Askew, David (2002-04-04). "The Nanjing Incident: Recent Research and Trends". Archived from the original on 2018-04-05.
- ^ a b Paragraph 2, p. 1012, Judgment International Military Tribunal for the Far East.
- ^ 1937 Japanese Field Commander's Map of the Battle of Shanghai, China geographicus.com Retrieved 22 April 2020
- ^ The Nanjing Massacre exequy.wordpress.com Retrieved 22 April 2020
- ^ Rabe, John, and Erwin Wickert. 1998. The Good Man of Nanking: The Diaries of John Rabe. New York: A. A. Knopf. pp. 56, 59–60.
- ^ "War and reconciliation: a tale of two countries". The Japan Times Online. Retrieved 2011-03-06.
- ^ Cummins, Joseph. 2009. The World's Bloodiest History. p. 149.
- ^ Honda, Katsuichi, and Frank Gibney. "The Nanjing massacre: a Japanese journalist confronts Japan's national shame." pp. 39–41.
- ^ Tokyo Nichi Nichi, 13 December 1937 article on the killing contest.
- ^ Japan Advertiser, 7 December 1937 (an American-owned and edited English-language daily paper in Tokyo)
- ^ Kingston 2008, p. 9.
- ^ Wakabayashi, Bob Tadashi (Summer 2000). "The Nanking 100-Man Killing Contest Debate: War Guilt Amid Fabricated Illusions, 1971–75". The Journal of Japanese Studies. 26 (2): 307–340. doi:10.2307/133271. JSTOR 133271.
- ^ "Jurist – Paper Chase: Japanese court rules newspaper didn't fabricate 1937 Chinese killing game". Jurist.law.pitt.edu. 2005-08-23. Archived from the original on February 25, 2011. Retrieved 2011-03-06.
- ^ "楽天が運営するポータルサイト : 【インフォシーク】Infoseek". infoseek.co.jp. Archived from the original on May 12, 2006.
- ^ "The scars of Nanking: Memories of a Japanese outrage". The Independent. London. December 13, 2007. Archived from the original on January 28, 2012. Retrieved August 22, 2017.
- ^ a b "Five Western Journalists in the Doomed City". Archived from the original on 2005-03-25. Retrieved 2006-04-19.
- ^ "Chinese Fight Foe Outside Nanking; See Seeks's Stand". Retrieved 2006-04-19.
- ^ "Japan Lays Gain to Massing of Foe". Retrieved 2006-04-19.
- ^ Askew, David (April 2002). "The International Committee for the Nanking Safety Zone: An Introduction" (PDF). Sino-Japanese Studies. 14: 3–23.
- ^ "Genocide in the 20th Century: The Rape of Nanking 1937–1938 (300,000 Deaths)". History Place. Retrieved 27 March 2017.
- ^ Bergamini, David. Japan's Imperial Conspiracy. p. 23.
- ^ Bergamini, David. Japan's Imperial Conspiracy. p. 24.
- ^ a b Chen, World War II Database
- ^ David Bergamini, Japan's imperial Conspiracy, 1971, p. 24
- ^ Iris Chang, The Rape of Nanking, 1997, p. 40
- ^ Akira Fujiwara, "Nitchū Sensō ni Okeru Horyo Gyakusatsu2, Kikan Sensō Sekinin Kenkyū 9, 1995, p. 22
- ^ Kajimoto, Masato. "Battle of Shanghai". Archived from the original on 2006-02-05. Retrieved 2006-04-19.
- ^ a b Yoshiaki Itakura, 本当はこうだった南京事件 (Tokyo: Nihon Tosho Kankokai, 1999), 11.
- ^ Suping Lu (2019). The 1937–1938 Nanjing Atrocities. p. 33. ISBN 978-9811396564.
- ^ Vautrin, Minnie (2008). Terror in Minnie Vautrin's Nanjing: Diaries and Correspondence, 1937–38. University of Illinois Press. ISBN 978-0-252-03332-2. Retrieved 15 April 2020.
- ^ "Special Report: How the Nanjing Massacre became a weapon | GRI". Global Risk Insights. 27 October 2016. Retrieved 2021-03-19.
- ^ "Basic Facts on the Nanking Massacre and the Toyoko War Crimes Trial". Retrieved 26 January 2017.
- ^ Wakabayashi 2000, p. 319.
- ^ 国防部审判战犯军事法庭对战犯向井敏明等人的判决书. 民国史档案资料丛书—侵华日军南京大屠杀档案. 1947年12月18日: pp. 616–621.
- ^ a b c Drea, Edward (2006). Researching Japanese War Crimes. National Archives and Records Administration for the Nazi Warcrimes and Japanese Imperial Government Records Interagency Working Group. p. 9.
- ^ a b Drea, Edward (2006). Researching Japanese War Crimes. National Archives and Records Administration for the Nazi Warcrimes and Japanese Imperial Government Records Interagency Working Group. p. 10.
- ^ Drea, Edward (2006). Researching Japanese War Crimes. National Archives and Records Administration for the Nazi Warcrimes and Japanese Imperial Government Records Interagency Working Group. p. 28.
- ^ Drea, Edward (2006). Researching Japanese War Crimes. National Archives and Records Administration for the Nazi Warcrimes and Japanese Imperial Government Records Interagency Working Group. p. 28.
- ^ Drea, Edward (2006). Researching Japanese War Crimes (PDF). National Archives and Records Administration for the Nazi Warcrimes and Japanese Imperial Government Records Interagency Working Group. p. x.
- ^ Drea, Edward (2006). Researching Japanese War Crimes. National Archives and Records Administration for the Nazi Warcrimes and Japanese Imperial Government Records Interagency Working Group. p. x.
- ^ John G. Gagee, Case 9, Film 4, Folder 7, Box 263, Record Group 8, Special Collection, Yale Divinity School Library, cited in Suping Lu. They were in Nanjing: the Nanjing Massacre witnessed by American and British nationals. Hong Kong University Press, 2004
- ^ John Rabe, Erwin Wickert. The good man of Nanking: the diaries of John Rabe. A.A. Knopf, 1998. pp. 281–282. 2008. Retrieved 2011-03-06.
- ^ "HyperWar: International Military Tribunal for the Far East [Chapter 8]". www.ibiblio.org.
- ^ "Japanese Imperialism and the Massacre in Nanjing: Chapter X: Widespread Incidents of Rape". Museums.cnd.org. Retrieved 2011-03-06.
- ^ "A Debt of Blood: An Eyewitness Account of the Barbarous Acts of the Japanese Invaders in Nanjing." Dagong Daily (Wuhan ed.). 7 February 1938.; as quoted by Xingzu, Gao, Wu Shimin, Hu Yungong, and Cha Ruizhen. [1962] 1996. "Widespread Incidents of Rape." Ch. 10 in Japanese Imperialism and the Massacre in Nanjing, translated by R. Grey.
- ^ Hua-ling Hu, American Goddess at the Rape of Nanking: The Courage of Minnie Vautrin, 2000, p. 97
- ^ Documents on the Rape of Nanking, p. 254.
- ^ Zhang, Kaiyuan. 2001. Eyewitness to Massacre: American Missionaries Bear Witness to Japanese Atrocities in Nanjing. M. E. Sharpe.
- ^ Woods, John E. (1998). The Good Man of Nanking, the Diaries of John Rabe. p. 77.
- ^ Choy, Christine (director) (1997). In the Name of the Emperor (Documentary). New York: Filmmakers Library.
- ^ Yang Daqing, "Convergence or Divergence? Recent Historical Writings on the Rape of Nanjing", The American Historical Review 104 (1999), p. 7.
- ^ Chang, The Rape of Nanking, p. 95, citing:
- Shuhsi Hsu, Documents of the Nanking Safety Zone
- ^ Chang, The Rape of Nanking, p. 89, citing:
- Catherine Rosair, For One Veteran, Emperor Visit Should Be Atonement;
- George Fitch, Nanking Outrages;
- Li En-han, Questions of How Many Chinese Were Killed by the Japanese Army in the Great Nanking Massacre
- ^ Chang, Iris. 1997. The Rape of Nanking. Penguin Books. p. 95.
- ^ Chang, Iris (2014). The Rape of Nanking: The Forgotten Holocaust of World War II. ISBN 978-0465028252.
- ^ a b Marquand, Robert (August 20, 2001) "Why the Past Still Separates China and Japan", Christian Science Monitor states an estimate of 300,000 dead.
- ^ a b "HyperWar: International Military Tribunal for the Far East (Chapter 8) (Paragraph 2, p. 1015, Judgment International Military Tribunal for the Far East)".
- ^ Library of Congress, ed. (1964–1974). "25 July 1946. Prosecution's Witnesses. Wilson, Dr. Robert O.". Record of proceedings of the International Military Tribunal for the Far East. p. 2538.
- ^ Campbell, Bradley (June 2009). "Genocide as social control". Sociological Theory. 27 (2): 154. doi:10.1111/j.1467-9558.2009.01341.x. JSTOR 40376129. S2CID 143902886.
Also, genocide may occur in the aftermath of warfare when mass killings continue after the outcome of a battle or a war has been decided. For instance, after the Japanese occupied Nanjing in December 1937, Japanese soldiers massacred over 250,000 residents of the city.
- ^ Jean-Louis, Margolin (2006). "Japanese Crimes in Nanjing, 1937–38 : A Reappraisal". China Perspectives. 2006. doi:10.4000/chinaperspectives.571.
- ^ a b c Woods, John E. (1998). The Good Man of Nanking, the Diaries of John Rabe. pp. 67, 187, 281.
- ^ english.peopledaily.com.cn, Author on Nanjing loses libel appeal, search.japantimes.co.jp
- ^ Yang, Celia (2006). "The Memorial Hall for the Victims of the Nanjing Massacre: Rhetoric in the Face of Tragedy" (PDF). p. 310. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2007-06-12.
- ^ Japan's Last Vets of Nanking Massacre Open Up Archived 2017-01-16 at Wikiwix, Yahoo! News
- ^ Yang, Celia (2006). "The Memorial Hall for the Victims of the Nanking Massacre: Rhetoric in the Face of Tragedy" (PDF). p. 310. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2007-06-12. Author refers to source as Yin, James. (1996) The Rape of Nanking: An Undeniable History in Photographs. Chicago: Innovative Publishing Group, p. 103.
- ^ Lei, Wan (February 2010). "The Chinese Islamic "Goodwill Mission to the Middle East" During the Anti-Japanese War". DÎVÂN DİSİPLİNLERARASI ÇALIŞMALAR DERGİSİ. cilt 15 (sayı 29): 139–141. Retrieved June 19, 2014.
- ^ Van Ells, Mark D. (14 July 2009). "Nanjing, China".
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ Bristow, Michael (2007-12-13). "Nanjing remembers massacre victims". BBC News. Retrieved 2007-12-13.
- ^ Durdin, F. Tillman. "Japanese Atrocities Marked Fall of Nanking After Chinese Command Fled." New York Times (New York), January 9, 1938; accessed March 12, 2016.
- ^ Hua-ling Hu, American Goddess at the Rape of Nanking: The Courage of Minnie Vautrin, 2000, p. 77.
- ^ CBI Roundup, 16 December 1943, Rape of Nanking described by Missionary, cbi-theater-1.home.comcast.net Archived July 23, 2011, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Chang, Iris. The Rape of Nanking, Penguin Books, 1997, p. 162.
- ^ Woods, John E. (1998). The Good Man of Nanking, the Diaries of John Rabe. p. 271.
- ^ Chang, Iris, The Rape of Nanking: The forgotten holocaust of World War II, Basic Books, A Subsidiary of Perseus Books, L.L.C., 1997 pp. 105–139, the chapter on the Safety Zone
- ^ Woods, John E. (1998). The Good Man of Nanking, the Diaries of John Rabe. p. 274.
- ^ a b Woods, John E. (1998). The Good Man of Nanking, the Diaries of John Rabe. pp. 275–278.
- ^ John Rabe Archived 2013-07-22 at the Wayback Machine, moreorless
- ^ "John Rabe's letter to Hitler, from Rabe's diary" Population of Nanking, Jiyuu-shikan.org Archived December 29, 2010, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Spence, Jonathan D. (1999) The Search for Modern China, W.W. Norton and Company. p. 424; ISBN 0393973514.
- ^ Chapel, Joseph (2004). "Denial of the Holocaust and the Rape of Nanking".
- ^ Man, Chi-Wei (2012). "The Rape of Nanking vs. the incident of Nanking: a Literature Review". Momentum. University of Pennsylvania. 1 (1) – via Penn Libraries.
- ^ Chang, Iris. The Rape of Nanking: The Forgotten Holocaust. pp. 51–52.
- ^ Shinsho Hanayama, The Way of Deliverance: Three Years with the Condemned Japanese War Criminals (New York: Scribner, 1950), 185–186. OCLC 1527099
- ^ a b c Drea, Edward (2006). Researching Japanese War Crimes (PDF). National Archives and Records Administration for the Nazi Warcrimes and Japanese Imperial Government Records Interagency Working Group. p. 9.
- ^ a b Yang Daqing, "Convergence or Divergence? Recent Historical Writings on the Rape of Nanjing", The American Historical Review 104 (1999)
- ^ Drea, Edward (2006). Researching Japanese War Crimes (PDF). National Archives and Records Administration for the Nazi Warcrimes and Japanese Imperial Government Records Interagency Working Group. p. 21.
- ^ Drea, Edward (2006). Researching Japanese War Crimes. National Archives and Records Administration for the Nazi Warcrimes and Japanese Imperial Government Records Interagency Working Group. p. 17.
- ^ Iwanami Shinsho, Fujiwara Akira (editor). Nankin jiken O Dou Miruka, 1998, Aoki shoten, ISBN 4250980162, p. 18.
- ^ Yoshida, Hiroshi. Nankin jiken o dou miruka p. 123, Tennou no guntai to Nankin jiken 1998, Aoki shoten, p. 160; ISBN 4250980197.
- ^ Takashi Yoshida, The Making of the "Rape of Nanking" (New York: Oxford University Press, 2006), 60.
- ^ Yang, Daqing (2001). "Convergence or Divergence? Recent Historical Writings on the Rape of Nanjing". Perennial. 104 (3): 842–865. doi:10.2307/2650991. ISBN 9780060931308. JSTOR 2650991.
- ^ Tokushi Kasahara. "Le massacre de Nankin et les mécanismes de sa négation par la classe politique dirigeante" [The Nanjing Massacre and the mechanisms of its negation by the political ruling class] (PDF). ihtp.cnrs.fr (in French).[dead link]
- ^ Masahiro Yamamoto, Nanking: Anatomy of an Atrocity (Westport, Connecticut: Praeger, 2000), p. 193.
- ^ Ono Kenji, "Massacre Near Mufushan," in The Nanking Atrocity, 1937–38: Complicating the Picture, ed. Bob Tadashi Wakabayashi (New York: Berghahn Books, 2008), p. 85.
- ^ Masahiro Yamamoto, Nanking: Anatomy of an Atrocity (Westport, Connecticut: Praeger, 2000), 112.
- ^ a b Bob Tadashi Wakabayashi, "Leftover Problems," in The Nanking Atrocity, 1937–38: Complicating the Picture, ed. Bob Tadashi Wakabayashi (New York: Berghahn Books, 2008), 382–384.
- ^ David Askew, "The Scale of Japanese Atrocities in Nanjing: An Examination of the Burial Records," Ritsumeikan Journal of Asia Pacific Studies, June 2004, 7–10.
- ^ a b "Nanking Atrocities – In the 1990s". nankingatrocities.net. Archived from the original on October 26, 2013.
- ^ U.S. Archives Reveal War Massacre of 500,000 Chinese by Japanese Army Archived 2007-12-13 at the Wayback Machine.
- ^ United States Department of State, ed. (1954). Foreign relations of the United States diplomatic papers, 1937. The Far East. Vol. 3. U.S. Government Printing Office. p. 806.
- ^ a b "Japanese statement protesting UNESCO registration of Nanjing Massacre docs backfires". Archived from the original on 26 November 2015. Retrieved 25 November 2015.
- ^ Yang Daqing, "Convergence or Divergence? Recent Historical Writings on the Rape of Nanjing", The American Historical Review 104 (1999), p. 4.
- ^ Herbert Bix, Hirohito and the Making of Modern Japan, 2000, p. 583
- ^ John W. Dower, Embracing Defeat: Japan in the Wake of World War II, 1999, p. 326.
- ^ Thomas M. Huber, Japan's Battle of Okinawa, April–June 1945, Leavenworth Papers Number 18, Combat Studies Institute, 1990, p. 47
- ^ "「松井石根研究会」の必要性について". history.gr.jp. Archived from the original on July 21, 2011.
- ^ "Hisao Tani". Archived from the original on February 18, 2010. Retrieved March 26, 2009.
- ^ Awaya Kentarô, Yoshida Yutaka, Kokusai kensatsukyoku jinmonchôsho, dai 8 kan, Nihon Tosho Centâ, 1993., Case 44, pp. 358–366.
- ^ a b Bix, Herbert (2001). "Hirohito and the Making of Modern Japan". Perennial: 734. ISBN 978-0060931308.
- ^ Dower, John (2000). Embracing defeat: Japan in the wake of World War II (Paperback ed.). New York: Norton. p. 459. ISBN 978-0393320275.
- ^ Brackman, Arnold C. (1988). The other Nuremberg: the untold story of the Tokyo war trials. New York: Quill. p. 395. ISBN 0688079571.
- ^ a b Yang, Daqing (June 1999). "Convergence or Divergence? Recent Historical Writings on the Rape of Nanjing". The Journal of Japanese Studies. 104 (3): 857. doi:10.2307/2650991. JSTOR 2650991. PMID 19291890.
- ^ "More names on Nanjing Massacre memorial wall". www.china.org.cn.
- ^ "Religious Assembly Held to Mourn Nanjing Massacre Victims".
- ^ AFP (December 13, 2014). "China holds first Nanjing Massacre memorial day". Telegraph.co.uk. Archived from the original on 2022-01-10.
- ^ Xinhua (October 9, 2015). "Documents of Nanjing Massacre added to UNESCO's Memory of World Register". Global Post. Archived from the original on October 10, 2015. Retrieved October 10, 2015.
- ^ "Japan's Apologies for World War II". The New York Times. 14 Aug 2015. Retrieved 9 May 2019.
- ^ McDonell, Stephen (12 Aug 2015). "Rape of Nanking: Japan's WWII apology to reopen old wounds with China". ABC News. Retrieved 9 May 2019.
- ^ "Special Report: How the Nanjing Massacre became a weapon | GRI". Global Risk Insights. 2016-10-27. Retrieved 2021-01-25.
- ^ Chang, Jung; Jon Halliday (2005). Mao: The Unknown Story (1st American ed.). New York: Knopf. p. 207. ISBN 0679422714. OCLC 57357425.
- ^ "The Nanking Massacre: Fact Versus Fiction". Retrieved 2008-05-06.
- ^ Honda, Katsuich. "Chūgoku no Tabi" (中国の旅), "Travels in China"". Asahi Shimbun.
- ^ Yamamoto, Shichihei (March 1972). "Reply to Katsuichi Honda". Every Gentlemen.
- ^ Suzuki, Akira (April 1972). "The Phantom of The Nanjing Massacre". Every Gentlemen.
- ^ Kingston, Jeff. March 1, 2014. "Japan's reactionaries waging culture war." Japan Times.
- ^ "A (very) short history of Japan's war apologies". The Washington Post. ISSN 0190-8286. Retrieved 13 August 2021.
- ^ "I'm Sorry?". NewsHour with Jim Lehrer. December 1, 1998. Archived from the original on February 22, 2008.
- ^ Gallicchio, Marc S. 2007. The Unpredictability of the Past. p. 158.
- ^ Yoshida, Takashi. 2006. The Making of the 'Rape of Nanking'. pp. 157–158.[ISBN missing]
- ^ Jun Hongo (23 February 2012). "Nagoya mayor won't budge on Nanjing remark". Japan Times.
- ^ "Japan ruling MPs call Nanjing massacre fabrication". 2007-06-19. Archived from the original on May 22, 2009. Retrieved 2009-03-19.
- ^ "Subcommittee on Nanjing Issues Press Conference (YouTube)". YouTube. 2007-06-19. Archived from the original on June 25, 2014. Retrieved 2010-11-23.
- ^ Josh Chin & Yoree Koh (February 22, 2012). "Japanese Official Denies Nanjing Massacre". Wall Street Journal.
- ^ Hongo, Jun, "Nagoya mayor won't budge on Nanjing remark", Japan Times, 23 February 2012, p. 2.
- ^ "Tokyo governor backs Nanjing massacre denial". AFP. February 24, 2012. Archived from the original on February 25, 2012.
- ^ Kasahara, Tokushi (2007). "The Nanking 100-man killing contest debate". The Nanking atrocity, 1937–38 : complicating the picture. Oxford: Berghahn. p. 143. ISBN 978-1845451806.
- ^ "Governor of Japan broadcaster NHK denies Nanjing massacre". BBC. February 4, 2014.
- ^ "百田氏が選挙応援演説 NHK経営委員、持論展開". 47news.jp. 共同通信社. 2014-02-05. Archived from the original on February 7, 2014. Retrieved 2014-02-08.
- ^ Yuan 2004
- ^ Pu, Xiaoyu (2005-09-30). "The Nanking Massacre, Justice and Reconciliation: A Chinese Perspective" (PDF). Perspectives. 6 (3). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2009-03-25. Retrieved 2009-03-21.
- ^ Yoshida, Takashi. The Making of the Rape of Nanking: History and Memory in Japan, China, and the United States (New York: Oxford University Press, 2006), p. 5.
- ^ "Fury as Koizumi honours war dead". The Age. Melbourne. August 15, 2006.
- ^ "In Japan, denial over Nanjing still holds sway after 70 years". The Christian Science Monitor. Retrieved 2011-03-06.
- ^ Mao, Yushi (2014). "Lessons from China's Great Famine" (PDF). CATO Journal. 34 (3): 486.
- ^ Monk, Paul (1997). "Book review. 'Hungry Ghosts: Mao's Secret Famine' by Jasper Becker". The China Journal. 38: 201–202. doi:10.2307/2950355. JSTOR 2950355.
- ^ Brown, Clayton D. (2014). "Book review. 'Tombstone: The Great Chinese Famine, 1958–1962' by Yang Jisheng". Education About Asia. 19 (2): 92.
- ^ Martina, Michael (2014-07-03). "China cites Japan wartime 'confessions' in propaganda push". Reuters.
- ^ Mirsky, Jonathan (1998-12-02). "The Chinese, Too, Have Much to Apologize For". New York Times.
- ^ Hillenbrand, Margaret (2020). Negative exposures : knowing what not to know in contemporary China. Duke University Press. p. xix.
- ^ Yoshida, Takashi (2006). The Making of the "Rape of Nanking". p. 5. ISBN 978-0195180961.
- ^ Yoshida, Takashi (2006). The Making of the 'Rape of Nanking'.
- ^ "Ministry of Foreign Affairs of Japan". Retrieved 15 June 2015.
- ^ "Japanese statement protesting UNESCO registration of Nanjing Massacre docs backfiresCanada ALPHA 加拿大史維會". www.alpha-canada.org.
- ^ "China athletes unlikely to stay at controversy-linked Sapporo hotel".
- ^ McCurry, Justin (2015-10-13). "Japan threatens to halt Unesco funding over Nanjing massacre listing". The Guardian.
- ^ "ついに馬脚現した習近平、歴史歪曲が白日の下に 南京虐殺の捏造がついに暴かれ始めた | JBpress (ジェイビープレス)". JBpress(日本ビジネスプレス) (in Japanese). Retrieved 2021-11-02.
- ^ "音を立てて崩れ始めた「南京大虐殺」の嘘 虚構が生き残る道は中国の政治的主張のみに | JBpress (ジェイビープレス)". JBpress(日本ビジネスプレス) (in Japanese). Retrieved 2021-11-02.
- ^ "南京大虐殺"決定的証拠写真" 全てがおそらく合成かヤラセ". NEWSポストセブン (in Japanese). Retrieved 2021-11-02.
- ^ "The spin in history textbooks". 2015-08-16. Retrieved 15 September 2015.
- ^ Oi, Mariko (14 March 2013). "What Japanese history lessons leave out". BBC.
- ^ Wang, Zheng (23 April 2014). "History Education: The Source of Conflict Between China and Japan". The Diplomat.
- ^ Askew, David (2002-04-04). "The Nanjing Incident – Recent Research and Trends". Archived from the original on 2018-04-05. Retrieved 2009-03-21.
- ^ Qian, Fengqi; Liu, Guoqiang (2019). "Remembrance of the Nanjing Massacre in the Globalised Era: The Memory of Victimisation, Emotions and the Rise of China". China Report. 55 (2): 86–88. doi:10.1177/0009445519834365. S2CID 159087909.
- ^ Wang, Zheng (2012). Never Forget National Humiliation: Historical Memory in Chinese Politics and Foreign Relations. Columbia University Press. pp. 85–89.
- ^ French, Howard W. (2017). Everything under the Heavens: How the past helps shape China's push for global power. Knopf. pp. 201–203.
- ^ Jones, Paul. "2001 ASSLH conference – Chinese seamen and Australian labour: The mass desertion from the SS Silksworth at Newcastle, October 1937". Retrieved 26 September 2013.
- ^ "Nanjing massacre victims named". BBC News. 2007-12-04. Retrieved 2007-12-04.
Sources
- Chang, Iris, The Rape of Nanking: The Forgotten Holocaust of World War II, Foreword by William C. Kirby; Penguin US (Paper), 1998; ISBN 0140277447
- Fogel, Joshua A. (2000). The Nanjing Massacre in history and historiography. Berkeley, CA: University of California Press. p. 248. ISBN 978-0520220072.
Further reading
- Askew, David. "The International Committee for the Nanking Safety Zone: An Introduction" Sino-Japanese Studies Vol. 14, April 2002 (Article outlining membership and their reports of the events that transpired during the massacre)
- Askew, David, "The Nanjing Incident: An Examination of the Civilian Population" Sino-Japanese Studies Vol. 13, March 2001 (Article analyzes a wide variety of figures on the population of Nanking before, during, and after the massacre)
- Bergamini, David, "Japan's Imperial Conspiracy," William Morrow, New York; 1971.[ISBN missing]
- Brook, Timothy, ed. Documents on the Rape of Nanjing, Ann Arbor: The University of Michigan Press, 1999. ISBN 0472111345 (Does not include the Rabe diaries but does include reprints of "Hsū Shuhsi, Documents of the Nanking Safety Zone, Kelly & Walsh, 1939".)
- Hua-ling Hu, American Goddess at the Rape of Nanking: The Courage of Minnie Vautrin, Foreword by Paul Simon; 2000, ISBN 0809323036
- Fujiwara, Akira "The Nanking Atrocity: An Interpretive Overview" Japan Focus October 23, 2007.
- Galbraith, Douglas, A Winter in China, London, 2006. ISBN 0099465973. A novel focussing on the western residents of Nanking during the massacre.
- Harmsen, Peter. Nanjing 1937: Battle for a Doomed City. Philadelphia: Oxford: Casemate, 2015. ISBN 978-1612002842
- Higashinakano, Shudo, The Nanking Massacre: Fact Versus Fiction: A Historian's Quest for the Truth, Tokyo: Sekai Shuppan, 2005. ISBN 4916079124
- Higashinakano, Kobayashi and Fukunaga, Analyzing The 'Photographic Evidence' of The Nanking Massacre, Tokyo: Soshisha, 2005. ISBN 4794213816
- Honda, Katsuichi, Sandness, Karen trans. The Nanjing Massacre: A Japanese Journalist Confronts Japan's National Shame, London: M.E. Sharpe, 1999. ISBN 0765603357
- Hsū Shuhsi, ed. (1939), Documents of the Nanking Safety Zone (reprinted in Documents on the Rape of Nanjing Brook ed. 1999)[ISBN missing]
- Kajimoto, Masato "Mistranslations in Honda Katsuichi's the Nanjing Massacre" Sino-Japanese Studies, 13. 2 (March 2001) pp. 32–44
- Lu, Suping, They Were in Nanjing: The Nanjing Massacre Witnessed by American and British Nationals, Hong Kong University Press, 2004.[ISBN missing]
- Murase, Moriyasu,Watashino Jyugun Cyugoku-sensen(My China Front), Nippon Kikanshi Syuppan Center, 1987 (revised 2005). (includes disturbing photos, 149 page photogravure) ISBN 4889008365 (村瀬守保, 私の従軍中国戦線)
- Qi, Shouhua. When the Purple Mountain Burns: A Novel San Francisco: Long River Press, 2005. ISBN 1592650414
- Qi, Shouhua. Purple Mountain: A Story of the Rape of Nanking (A novel) English Chinese Bilingual Edition (Paperback, 2009) ISBN 1448659655
- Rabe, John, The Good Man of Nanking: The Diaries of John Rabe, Vintage (Paper), 2000. ISBN 0375701974
- Robert Sabella, Fei Fei Li and David Liu, eds. Nanking 1937: Memory and Healing (Armonk, NY: M.E. Sharpe, 2002). ISBN 0765608170.
- Wakabayashi, Bob Tadashi "The Nanking 100-Man Killing Contest Debate: War Guilt Amid Fabricated Illusions, 1971–75",The Journal of Japanese Studies, Vol. 26 No. 2 Summer 2000.
- Wakabayashi, Bob Tadashi The Nanking Atrocity, 1937–1938: Complicating the Picture, Berghahn Books, 2007, ISBN 1845451805
- Yamamoto, Masahiro Nanking: Anatomy of an Atrocity, Praeger Publishers, 2000, ISBN 0275969045
- Yang, Daqing. "Convergence or Divergence? Recent Historical Writings on the Rape of Nanjing" American Historical Review 104, 3 (June 1999). 842–865.
- Young, Shi; Yin, James. Rape of Nanking: Undeniable history in photographs Chicago: Innovative Publishing Group, 1997.[ISBN missing]
- Zhang, Kaiyuan, ed. Eyewitnesses to Massacre, An East Gate Book, 2001 (includes documentation of American missionaries M.S. Bates, G.A. Fitch, E.H. Foster, J.G. Magee, J.H. MaCallum, W.P. Mills, L.S.C. Smythe, A.N. Steward, Minnie Vautrin and R.O. Wilson.) ISBN 0765606844
External links
- The Rape of Nanking – Nanking Massacre – documentary
- Rape of Nanking videos
- Documents of Nanking Massacre – UNESCO
- BBC News: Nanking remembers massacre victims
- Online Documentary: The Nanking Atrocities Archived 2019-02-21 at the Wayback Machine A master's degree thesis that delves into the atrocity
- English translation of a classified Chinese document on the Nanking Massacre
- Japanese Imperialism and the Massacre in Nanking by Gao Xingzu, Wu Shimin, Hu Yungong, & Cha Ruizhen
- Kirk Denton, "Heroic Resistance and Victims of Atrocity: Negotiating the Memory of Japanese Imperialism in Chinese Museums"
- Nanking Massacre history site: History, Photos and Articles
- 'No massacre in Nanking,' Japanese lawmakers say
- "Denying Genocide: The Evolution of the Denial of the Holocaust and the Nanking Massacre," college research paper by Joseph Chapel, 2004
- Rape of Nanking Original reports from The Times
- War and reconciliation: a tale of two countries
- Review of Iris Chang, The Rape of Nanking: The Forgotten Holocaust of World War II
- The Ghosts of Nanking: Mogollon Connection Special Series by Jesse Horn Archived 2019-04-15 at the Wayback Machine
- The Nanking Massacre Project: A Digital Archive of Documents & Photographs from American Missionaries Who Witnessed the Rape of Nanking From the Special Collections of the Yale Divinity School Library
- The Nanking Incident: Recent Research and Trends by David Askew in the Electronic Journal of Contemporary Japanese Studies, April 2002
About the page
Presented content of the Wikipedia article was extracted in 2022-09-12 based on https://en.wikipedia.org/?curid=55066







![Prisoners being buried alive[88]](https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/67/Chinese_civilians_to_be_buried_alive.jpg/150px-Chinese_civilians_to_be_buried_alive.jpg)



![General Iwane Matsui[114]](https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/c/c1/Iwane_Matsui.jpg/110px-Iwane_Matsui.jpg)
![General Hisao Tani[115]](https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/c/c0/Tani_Hisao.jpg/123px-Tani_Hisao.jpg)



